Adriana Dias (Royal Holloway, University of London)
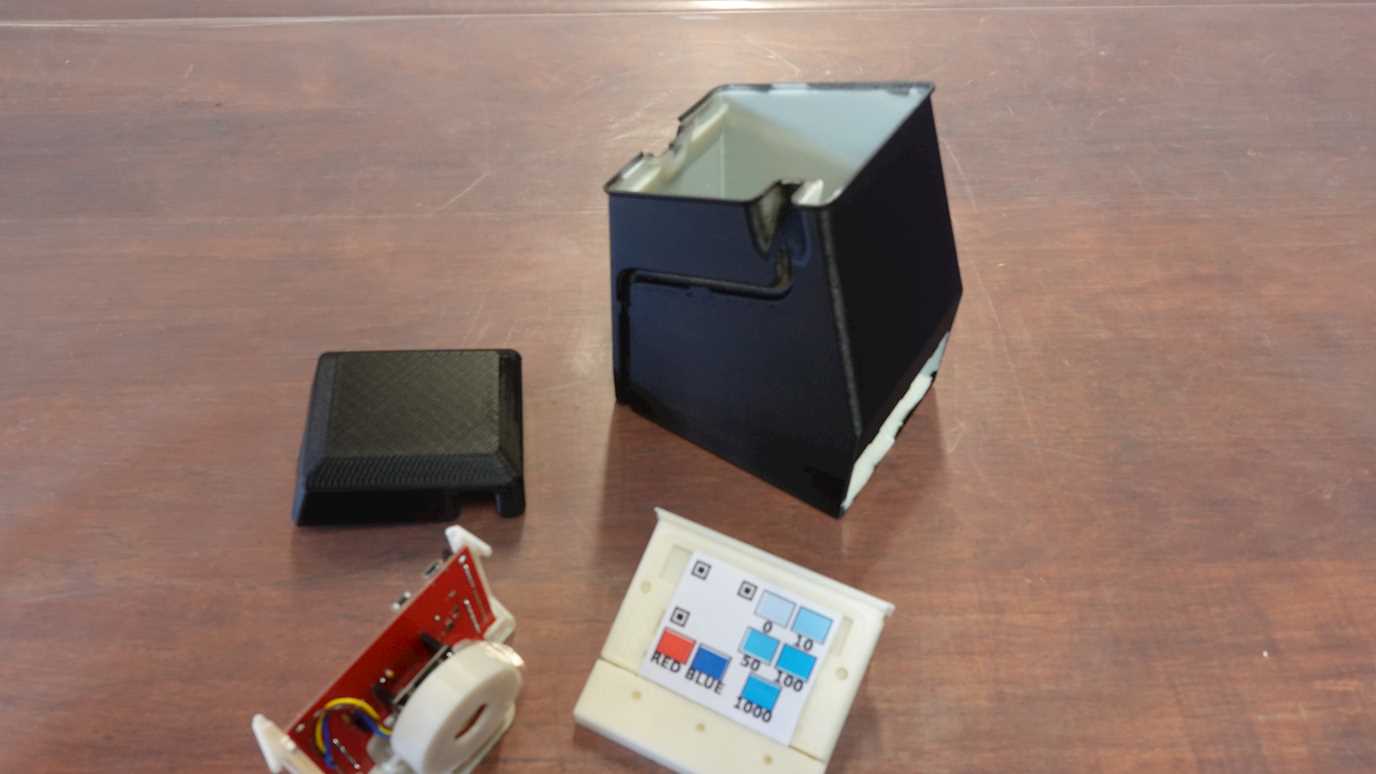
This talk reports on the development of a novel CMOS device employing lead-sensing bacteria to assay lead in drinking water. The objective of the PlomBOX project is to develop a low-cost sensor (£10) which can expedite access to on-demand assay methods and thus help mitigate lead intake through contaminated drinking water. The project follows three development paths: a) Certain bacteria can fluoresce or change colour when in the presence of lead. A genetically modified strain of Escherichia coli sensitive to lead concentrations up to 10 ppb is being developed. This constitutes the biosensor that fluoresces in proportion to the presence of lead. b) Bacteria response is imaged using a microprocessor (ESP32) with a camera module. This constitutes the optical metrology component of the PlomBOX. c) Data acquisition and control of the PlomBOX is achieved through a Bluetooth connection with the PlomApp, a custom-developed mobile phone application. Data are sent from the PlomApp to a database where a bespoke automated analysis software provides a result of the lead concentration in a sample of water. This talk reports on the instrumentation challenges of developing the electronics for the PlomBOX and on the first prototype.