Key information
Duration: 3 years full time
UCAS code: VV19
Institution code: R72
Campus: Egham
The course
Ancient and Medieval History (BA)
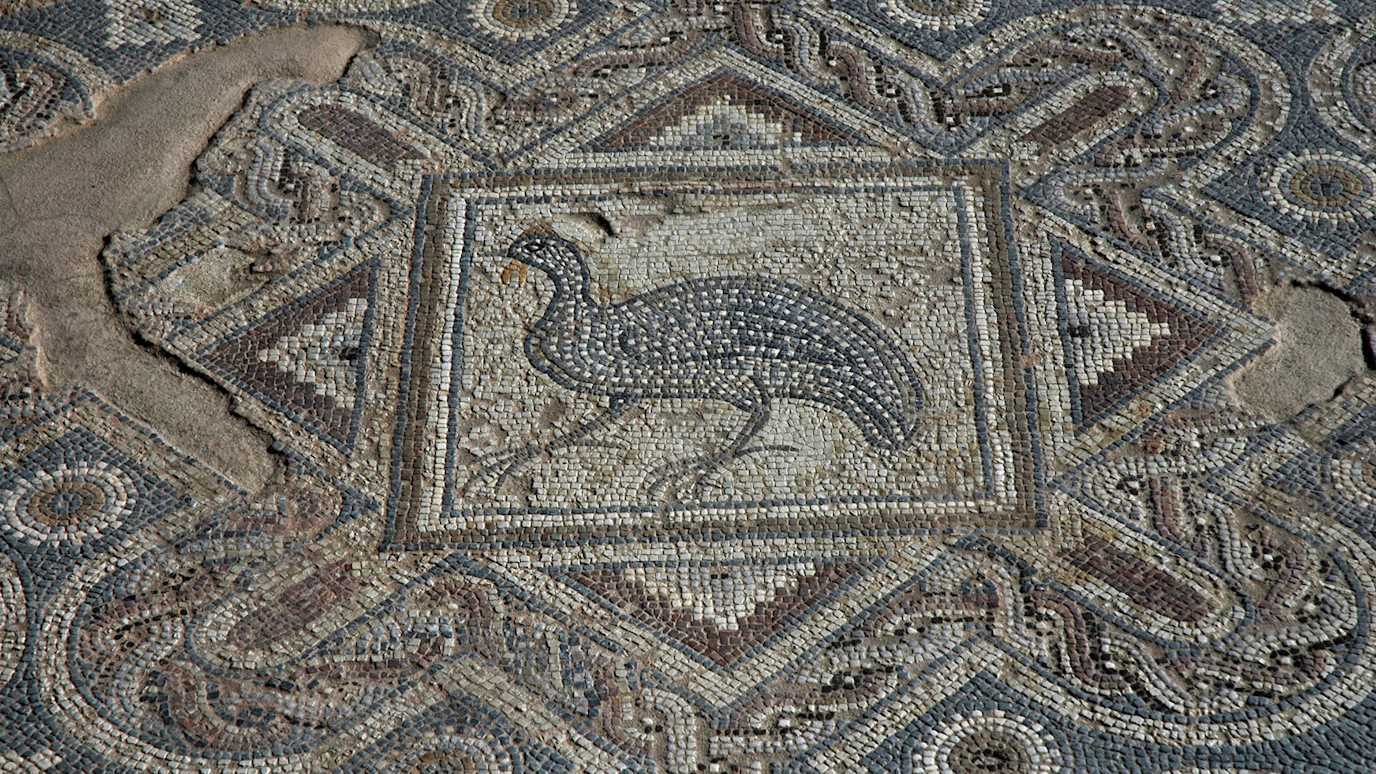
Drawing on expertise from our Classics and History departments, Ancient and Medieval History offers the opportunity to study the history of Greece and Rome in the Classical period (600 BCE - 700CE) and how that world developed into the Medieval period (c. 600 CE - 1400 CE). The course brings together the two key periods of pre-modern history, offering students the opportunity to compare and contrast pre-modern social and political systems and to develop the knowledge, theories and methodologies necessary for the study of these periods of history.
Taught by a variety of internationally recognised experts, Ancient History allows you will delve into the politics, events and developments underpinning our understanding of many aspects of historical societies and, indeed, our own culture. You will explore themes, key periods and problems in Greek and Roman history, such as the emergence (and fall) of democracy and the rise, decline and fall of Empires.
As a student of Ancient History you will be part of our Classics Department, where the quality of research that informs our teaching and a friendly, individual approach which shapes the way we guide our students combine to create an unbeaten academic experience. A thriving Classics Society contributes to the friendly and sociable atmosphere of the Classics department.
Studying Medieval History within the Department of History is exciting and rewarding; it encourages you to appreciate the human experience in other places and at other times, in a world whose consequences are with us still, be it through the development of international relations, the formation of geopolitical regions (Christendom/ the Islamic world), or the development of town life.
Our internationally renowned academics are developing the very latest thinking on historical problems; this cutting edge knowledge informs the curriculum and will enhance your learning experience. By studying History at one of the largest and most influential departments in the country you will be able to choose from an exceptionally broad range of subjects.
From time to time, we make changes to our courses to improve the student and learning experience. If we make a significant change to your chosen course, we’ll let you know as soon as possible.
Course structure
Core Modules
Year 1
-
History in the Making is Royal Holloway’s first year foundation History module. This module covers the broad sweep of human history, but it is not intended to provide a straightforward narrative from the ancient to the modern world. Instead, this module seeks to introduce our first-year students to an array of different topics and themes - from the rise of Christianity to the rise of modern nation states - that they will encounter again in the Gateway, Survey, Further and Special Subjects that they take during their degree. How have historians discussed themes like Revolution or Gender? What kinds of sources have they used to do so? These, and many other thought-provoking questions, are interrogated over the two terms of this module and explored from a global, rather than a simply “Western,” perspective. In moving forwards chronologically, this module also contemplates how our very understanding of what history is and what history is for has evolved. Finally, History in the Making encourages students to think about the practice and use of history beyond the academy, about how the wider public has engaged with, manipulated and consumed the past. This ‘public history’ dimension is present in a number of lectures across both terms and all students have the opportunity to explore these issues themselves in the group poster project and presentation. Although titled “History in the Making”, this module might easily have been called “Historians in the Making”, providing our students with the skills, methods and critical approach to the past that prove essential to successfully completing a university History degree.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the Greek World in the Classical Period. You will look at the key events in Greek History from 580 to 323 BC and place these in their historical context. You will consider historical problems and critically examine information and accounts set out in the Greek sources as well as in the works of modern historians. You will analyse a range of sources materials, including inscription, historiography and oratory, and develop an awareness of potential bias in these.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the development of Roman politics and society over the extended period of Roman history, from early Rome through to the emergence of the Medieval World. You will look at the chronology and development of Rome, examining key themes in the interpretation of particular periods of Roman history, including the rise and fall of the Republic and the Imperial Monarchy. You will consider the difficulties and methological issues in the interpretation of Roman Historiography and analyse a variety of theoretical approaches used by historians.
Year 2
- All modules are optional
Year 3
- All modules are optional
Optional Modules
There are a number of optional course modules available during your degree studies. The following is a selection of optional course modules that are likely to be available. Please note that although the College will keep changes to a minimum, new modules may be offered or existing modules may be withdrawn, for example, in response to a change in staff. Applicants will be informed if any significant changes need to be made.
Year 1
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the framework of Greek literary history from Homer to Heliodorus. You will look at the chronology of major authors and works, and how they fit into larger patterns in the development of Greek culture and political history. You will examine ancient literary texts in translation, considering issues in key genres including epic, lyric, drama, oratory, philosophical writing, historiography, Hellenistic poetry, and the Greek novel.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the history of Roman literature from its beginnings until the end of the Republic. You will look at the work of the major Republican Roman authors Plautus and Terence, Lucretius, Catullus and Cicero. You will consider the issues in the earlier history of Roman literature, including the relationship with Greek models and the question of Roman originality, literature and politics, the use of literature for scientific or philosophical exposition, and the development of narrative style ant attitudes to the Roman Republican past.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the history of Roman literature in the early imperial period. You will look at the work of five authors selected from the Julio-Claudian period, considering the ways in which Roman literature responded to the new political conditions established by the Principate. You will develop your skills in interpretation, analysis and argument as applied both to detailed study of texts (in translation) and to more general issues.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of ancient philosophical ideas and the ways in which philosophical arguments are presented and analysed. You will look at the thought and significance of the principal ancient philosophers, from the Presocratics to Aristotle, and examine sample texts such as Plato's 'Laches' and the treatment of the virtue of courage in Aristotle, 'Nicomachean Ethics' 3.6-9.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of how classical Greek and Roman societies developed the concept and role of the individual as part of the wider community. You will look at Greek and Roman education, and how that encouraged the formation of ideal behaviour and identity. You will consider the role of rhetoric, and how competition was encouraged within these societies though literary and dramatic contests, sport, military life, and religion. You will examine how these ideas reflect the role of the individual in the community of the cosmos, and the place in society of 'others', including the lower classes, women, children, the elderly, and slaves.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the Greek World in the Classical Period. You will look at the key events in Greek History from 580 to 323 BC and place these in their historical context. You will consider historical problems and critically examine information and accounts set out in the Greek sources as well as in the works of modern historians. You will analyse a range of sources materials, including inscription, historiography and oratory, and develop an awareness of potential bias in these.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of the development of Roman politics and society over the extended period of Roman history, from early Rome through to the emergence of the Medieval World. You will look at the chronology and development of Rome, examining key themes in the interpretation of particular periods of Roman history, including the rise and fall of the Republic and the Imperial Monarchy. You will consider the difficulties and methological issues in the interpretation of Roman Historiography and analyse a variety of theoretical approaches used by historians.
-
In this module you will develop an understanding of how different classical disciplines interrelate. You will focus on specific academic skills such as avoiding plagiarism, approaching and evaluating a range of ancient evidence, using library and other resources, critically evaluating modern scholarship and theoretical approaches, and relating academic study to employability.
-
This is a survey module covering a large and disparate field. No previous knowledge is assumed: it will offer a basic introduction to the principles of classical archaeology and to the archaeological material of ancient Greece. The module will help you to place archaeological objects and contexts alongside literature and philosophy and to gain a more rounded understanding of how the Greeks thought about their world and the physical environment they created for themselves. The main aim of the module is to familiarise you with the material culture of the Greek civilisation from the Bronze Age to the Hellenistic period. We will examine the principal forms of Greek art and architecture, together with their stylistic development and social context. We will also consider developments in political organisation and religious practice, as well as evidence for everyday life. The module will introduce basic methodological concepts and theoretical approaches to the study of ancient Greek material culture.
-
This module studies the broad spectrum of archaeological evidence for the Roman world. It will provide an introduction to the main sources of archaeological evidence and key sites across the Roman world. It will offer a taste of how we can use the evidence they provide in the study of history, society and technology during the period c. 200 BC – c. AD 300. It aims to familiarize you with the principal forms and contexts in which art and architecture developed in the Roman world; to introduce you to the uses of material culture in studying history, i.e. to study the art and architecture of Rome as part of its history, social systems, culture, and economy; and to develop critical skills in visual analysis.
-
This module investigates the origins of our ideas about human rights and duties, revolution and democracy, consent and liberty. Key original texts are studied, ranging from Plato and Aristotle in the ancient world to Machiavelli, More, Hobbes, Locke and the Enlightenment in the transition from the early modern to the modern world. The module takes a wide view of the boundaries of ‘European Political Thought’, also introducing several political thinkers from the Islamic world like al-Mawardi, Ibn Khaldun and Ibn Taymiyya. Like their Christian counterparts elsewhere, their work marked a close engagement with Greek philosophy, and explored the question of what the presence of an almighty creator God meant for the conduct of human politics. This module always keeps an eye on what the close and careful reading of classical texts has to offer for our understanding of politics in the present. Working with primary sources, rather than the learning of factual details, stands at the centre of both how the module is taught and how it is assessed.
-
The early modern period was an age of change. It has been seen by many as the beginning of modernity, for it witnessed the consolidation of both national monarchies and the central state, the split of Christianity with the emergence of the Reformation, the spread of Islam to the Balkans, European expansion into the ‘new world’, the introduction of print, and significant changes in patterns of consumption. This module assesses the impact that these processes had on the lives of ordinary early modern Europeans and on their ways of making sense of the changes in the world around them. For example, we examine how the process of state-building brought about a new culture of discipline and self-restraint in everyday life; how people’s attitudes to the sacred and standards of morality changed with the spread of the Reformation and Counter-Reformation. We ask whether the introduction of print revolutionised ordinary people’s access to information and knowledge, and whether the encounter with Native Americans stimulated the development of a separate European identity, perceived as superior. This module also addresses continuities and changes in the domestic and private spheres of individuals’ lives -- gender relations, patterns of family life, ideas about childhood and intimacy, attitudes to health and hygiene, birth and death. Throughout the emphasis is on the experience of ordinary people.
-
The terms ‘Middle Ages’ and ‘Medieval’ are often used to evoke a dark and bigoted world, wracked by war, pestilence and superstition and oppressed by tyrannical kings and scheming priests. The image is not entirely false as all those things certainly did happen in the Middle Ages. But then again, they also occurred in most other periods of human history, including the twentieth century. Those aspects aside, the period from c.400 to c.1500 saw Western Europe transform itself from the poorer part of the retreating Roman empire to a wealthy, sophisticated and dynamic society that was starting to explore the world far beyond its borders. This module explores some of the changes and developments that took place along the way and answers some of the questions that you may always have wanted to ask: What happened after the Roman empire fell? What was ‘feudalism’? How were castles and Gothic cathedrals built? Why did the Pope become so powerful? What were the Crusades? Why did the Hundred Years’ War go on for so long? How did Europe survive after losing as much as half its population in the Black Death? And does this remote era have any relevance whatsoever to the modern world?
Year 2
- Greek History to 404 BC
- Greek History from 403 to 322
- Greek Historiography
- Historiography of the Roman World
- Gender in Classical Antiquity
- Greek Law and Lawcourts
- Greek History to 322 BC
- Augustus: Propaganda and Power
- The Roman Republic: A Social and Economic History
- The Rise of the Roman Empire: An Economic and Social history
-
The Later Roman Empire module spans the four centuries that marked the end of classical antiquity and the rise of the early medieval world. The module opens with the transformation of the Roman empire under Diocletian (284-305) and Constantine (306-337), and with the conversion of Constantine, the first Christian emperor, in AD 312. Students explore the fundamental political, social and religious developments of the fourth century, which saw the emergence of a Christian Roman empire and the migration of the Goths and Huns towards the imperial frontier. We then compare the contrasting fortunes of the western and eastern regions of the empire in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the west imperial power collapsed under the waves of barbarian invasions, to be succeeded by the Germanic kingdoms of the Goths and Franks and by the rising prestige of the Roman papacy. Yet in the east the empire survived and reached a new peak during the attempted reconquest of the emperor Justinian (527-565), before triumphing in the last great conflict between the Roman and Persian empires with which this module concludes. These were centuries of dramatic change, accessible through an impressive combination of literary sources (read in translation) and material evidence, and the legacy of those changes exerted a profound influence on later history.
-
By the middle of the seventh century, the very existence of the Byzantium (also known as the Byzantine Empire) was in question. It had lost almost half its territory to the Arabs and even its capital city of Constantinople was now under direct threat. Yet the state not only weathered this period of crisis but revived and flourished so that by 1050, it was once more a major power in the region, stretching from southern Italy to Armenia. This module traces the reasons why it survived, how it reversed the long series of defeats and the profound changes that took place in its military organisation, society, religious life, art and culture. It also examines how one key to its success was the way in which it interacted with the world around it, particularly with the Islamic caliphate, western Europe and the Slavonic world. Although the Byzantines frequently fought their neighbours, they preferred where possible to influence them through diplomacy and conversion. Then in the later eleventh century, new enemies appeared on the borders and Byzantium began to contract once more, a series of events that was to provide the background for the later launch of the First Crusade in 1095.
-
In this period London grew from a town of 50,000 inhabitants to a capital city of some 200,000. The Reformation not only swept away ‘superstitious’ beliefs, but destroyed much of the fabric and topography of the medieval City - this module will consider how Londoners coped with these changes. How were Londoners fed and watered? How were crafts organised? How was the City governed?
-
The triumph of the First Crusade (1099) resulted in the establishment of a Latin Christian community in the Levant for almost two hundred years. This module is primarily concerned to examine how the settlers maintained their hold on a region which was spiritually, economically and politically important to the Byzantine empire and the Muslim world as well.
- Medicine and Society in Medieval Europe
-
The Roman Republic occupies a special place in the history of Western civilisation. From humble beginnings beside the river Tiber, the Romans expanded to dominate the classical world. Their armies defeated Carthage and the successors of Alexander the Great, and brought all the surrounding peoples under Roman rule. Yet the triumph of the Republic was also its tragedy. Political and socio-economic crisis plunged Rome into a descending spiral of civil war as rival warlords struggled for supremacy, until the Republican constitution collapsed and was replaced by the autocratic Roman empire. In this module, we explore the history of the Republic from the foundation of Rome to the murder of Julius Caesar on the Ides of March 44 BC. Students examine the social and political pressures that drove Rome to conquer her Mediterranean empire and the consequences of that expansion for the Romans and for the peoples they conquered. The major literary sources are discussed in translation, together with the evidence of archaeology and material culture which helps us to bring the ancient Romans to life.
-
For almost half a millennium, the Roman empire ruled over the ancient Mediterranean world. This module surveys the golden years of imperial Rome, from the achievement of sole rule by the first emperor Augustus (31 BC - AD 14) to the murder of Commodus (the white-clad emperor from Gladiator) in AD 192. At its peak, Rome’s empire spanned from Hadrian’s Wall in Britain south to North Africa and east to Syria, enclosing the Mediterranean Sea within a single dominion. We analyse the political, social and cultural developments under the emperors of the first and second centuries AD, and reassess their achievements and legacies: Claudius’ invasion of Britain, Nero’s cultured tyranny, the terrible efficiency of Domitian, Trajan the conqueror, and the philosophical Marcus Aurelius. We likewise explore fundamental themes that shaped the wider empire, including imperial frontier policy and administration, the process of Romanisation, and the nature of Roman religion. The evidence of art and architecture is examined, particularly the monuments from Rome herself and the wealth of material preserved in the buried town of Pompeii, alongside the major literary sources all readily available in English translation.
- The Pursuit of Power: Europe 1000-1250
-
This module examines a period of momentous change, which witnessed the Great Famine and Black Death kill perhaps half of Europe’s population, the consequences of endemic warfare rampaging across the continent, and outbreaks of popular revolt involving exceptional brutality. Lectures and seminars trace the major developments in the period.
-
This module examines the formation of the Mongol Empire and its impact on the social, political, and cultural life in Western Asia. While discussing the Mongols and their presence in Western Asia, we will also consider other intellectual and social changes that occurred in the late medieval period.
-
The Italian Renaissance is conventionally portrayed as a period of cultural and artistic renewal, economic prosperity and advanced political forms (republican governments). This module will verify the validity of this picture by considering the everyday experience of the men and women who inhabited the cities of Northern and Central Italy between 1350 and 1650 - political participation, class conflict, education, ways of inhabiting, material culture, crime and violence, gender relationships and sexual deviancy, devotion and the use of magic.
-
The approach of this module is firmly comparative, and the geographical scope is wide: from the British Isles to the Crusader States. The period c.1000–1250 in Europe saw many key developments, including: the establishment of universities and of the Inquisition; the persecution of heretics, religious minorities and of perceived sexual deviants; and the growth of vernacular literature.
-
Late medieval Christian Europe was a world of contrasts. Plague was endemic, but those lucky enough to survive enjoyed improving standards of living that rested in many parts of Europe on a flourishing economic life. This naturally affected life in cities, opening up opportunities for many.
-
This module examines the early modern history of Western Asia from 1500 to 1789. In terms of political history, this crucial period witnessed the formation of the regional empires, i.e. the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal empires in the Central Islamic lands - we examine the formation and transformation of these three empires through the prism of the social, religious, and intellectual changes in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
-
The Independent Research Project offers students with a rewarding opportunity to develop their research and analytical skills. They can either write a longer-form 4000-word essay, which is a valuable stepping-stone towards the final year Dissertation, or produce a series of blog posts as a ‘Public History’ project suitable for a general audience. Each student’s Independent Research Project is linked to their chosen Further Subject module [see below], and they are supervised by their Further Subject tutor. In conjunction with their supervisor, students develop a research topic of their choosing. Emphasis is placed on primary source analysis, together with engaged with relevant historiographic debates among historians.
Year 3
-
The Extended Essay is a unit of independent study under the supervision of a member of staff. Students are required to write a long essay of 8,000 to 10,000 words.
- Greek Law and Lawcourts
- Augustus
- The Roman Republic: A Social and Economic History
- The Rise of the Roman Empire: An Economic and Social history
- Alexander the Great
- The City from Augustus to Charlemagne: The Rise and Fall of Civilisation
-
This module covers the crucial transitional period in which Christianity came to dominate the Mediterranean world, from the accession of the first Christian Roman emperor Constantine in 306 to the death of Augustine of Hippo in 430. The fundamental political, social and religious changes that took root during these dramatic years, which also witnessed the early Germanic invasions into the Roman empire, are brought to life by a broad spectrum of translated literary texts and material culture. Students engage with a wide selection of influential writers: Eusebius of Caesarea (Constantine’s biographer), the last pagan emperor Julian ‘the Apostate’, the historian Ammianus Marcellinus, the orator and teacher Libanius, and the Church fathers Jerome (with his ascetic circle of female students) and Augustine (author of the Confessions and City of God). We also examine other forms of evidence: the laws of the Theodosian Code, the inscriptions left by the Roman senatorial aristocracy, and an array of surviving examples of Late Roman art and architecture. The scope and diversity of these sources reflect the transformations of the period itself and offer dissertation opportunities for students with interests ranging from religious and political history to gender studies or the Roman empire’s ‘Decline and Fall’.
-
Pope Innocent III (1198-1216) was obsessed with crusading and he dedicated his pontificate to defeating the enemies of the Church. A profound challenge to his authority came from the Cathars of southern France - men and women following an austere lifestyle and holding a dualist belief in a Good God and an Evil God. Using a series of vivid contemporary narratives, in conjunction with other documents (including inquisitorial records), this course examines the beliefs and organisation of the Cathars and the progress of the Crusade and the Inquisition against them.
-
This course scrutinises an area of English social history that was once universally disparaged. Recent work, however, suggests that the Church in England from c1375-c1525 displayed remarkable resource in adapting to and satisfying the needs of contemporaries. As well as surveying some of the more vibrant areas of the Church’s institutional life, the course will dwell on the laity’s response, particularly as expressed through the parish. This will provide the opportunity to delve into areas such as popular belief and practice, parish government, and more informal activity in the foundation and management of lay confraternities.
-
The capture of the capital of the Byzantine empire (also known as Byzantium) by the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II (1451-1481) on 29 May 1453, was one of the pivotal events of the later Middle Ages. The module opens with a survey of the background: the decline of Byzantium, the rise of the Ottoman Turks and importance of the Italian maritime republics of Genoa and Venice. It then turns to the unsuccessful Ottoman attack on Constantinople in 1422, the subsequent Byzantine bid to secure western military aid at the Council of Ferrara/Florence, the disastrous crusade of Varna of 1443-4 and the lead-up to the final Ottoman attack. We make a detailed examination of the many contemporary accounts of the siege and consider their evidence as to why Mehmed II succeeded where so many others had failed in the past. Particular attention is paid to how eyewitnesses explained the disaster, and how they balanced metaphysical reasons such as the judgment of God and the wheel of fortune with practical ones, such as human weakness, the role of heavy cannon and a desire to blame anyone whom they disliked. Finally, the aftermath of the fall of Constantinople is examined: the call for a crusade to retake the city and the efforts of Pope Pius II to orchestrate a united response to the Turkish victory.
- Genghis Khan and His Empire, 1150-1300
-
This module takes students with GCSE level Latin up to Advanced Level knowledge of the language in one year. The objective of the module is to enable students to read Latin with reasonable fluency.
Teaching & assessment
The course has a modular structure, whereby students take 12 course units at the rate of four whole units per year. At least four course units of Ancient History must be taken over the three years of the degree, one at year 3 level and 3 course units of Medieval History, at least one at year 3 level. You will be able to mix Ancient and Medieval courses as suits your particular interests and develop your own specialisms within the flexible provision on offer.
You will be taught through a mixture of lectures, seminars and tutorials, depending on the subjects studied. Much of your work will be outside class: reading in the library or via e-learning resources (we have a comprehensive e-learning facility called Moodle). You will also be preparing for seminars and lectures, working on essays, and undertaking group projects and wide-ranging but guided independent study.
In your final year we provide ongoing support for your dissertation work, which usually includes:
- Lectures and practical sessions on Dissertation Research Methods e.g. planning your topics, carrying out research, using specialist resources, finding information in print and online, and managing your search results and references. These sessions are run in conjunction with the Library Service and are generally also open to second year students.
- Short departmental writing ‘surgeries’, in which academic staff offer general writing support if you experiencing problems and/or those who have specific queries.
Assessment takes place by a flexible combination of essays, projects, examinations and tests, various methods being employed depending on the nature of the course unit and the intended learning outcomes. In the third year, you complete a guided and extended piece of independent research, a 10,000 word dissertation on a historical subject.
Entry requirements
A Levels: ABB-BBB
Required subjects:
- At least five GCSEs at grade A*-C or 9-4 including English and Mathematics.
Where an applicant is taking the EPQ alongside A-levels, the EPQ will be taken into consideration and result in lower A-level grades being required. For students who are from backgrounds or personal circumstances that mean they are generally less likely to go to university, you may be eligible for an alternative lower offer. Follow the link to learn more about our contextual offers.
T-levels
We accept T-levels for admission to our undergraduate courses, with the following grades regarded as equivalent to our standard A-level requirements:
- AAA* – Distinction (A* on the core and distinction in the occupational specialism)
- AAA – Distinction
- BBB – Merit
- CCC – Pass (C or above on the core)
- DDD – Pass (D or E on the core)
Where a course specifies subject-specific requirements at A-level, T-level applicants are likely to be asked to offer this A-level alongside their T-level studies.
English language requirements
All teaching at Royal Holloway (apart from some language courses) is in English. You will therefore need to have good enough written and spoken English to cope with your studies right from the start.
The scores we require
- IELTS: 6.5 overall. Writing 7.0. No other subscore lower than 5.5.
- Pearson Test of English: 61 overall. Writing 69. No other subscore lower than 51.
- Trinity College London Integrated Skills in English (ISE): ISE III.
- Cambridge English: Advanced (CAE) grade C.
Country-specific requirements
For more information about country-specific entry requirements for your country please visit here.
Undergraduate preparation programme
For international students who do not meet the direct entry requirements, for this undergraduate degree, the Royal Holloway International Study Centre offers an International Foundation Year programme designed to develop your academic and English language skills.
Upon successful completion, you can progress to this degree at Royal Holloway, University of London.
Your future career
Our degree courses not only promote academic achievement but also the means to hone the life-skills necessary to excel, post-graduation.
Studying History both Ancient and Medieval requires research, assessment, reasoning, organization and self-management often on your own or as part of a team. So, by choosing to study this intellectually demanding discipline you will develop a broad range of skills which are highly prized by employers, including:
- the ability to communicate views and present arguments clearly and coherently
- the ability to critically digest, analyse and summarise content
- time management and the discipline to meet deadlines
- organisation and research skills
- problem-solving skills and capability
Being able to understand and process complex issues, to critically evaluate resources and construct coherent arguments both verbally and in writing is why many Royal Holloway classicists become employed in law, marketing, publishing, the media, government and finance. Employers like Channel 4, multinational law firm SJ Berwin, The Guildhall (City of London), accountancy firm KPMG, the Natural History Museum, Customs and Immigration, London Advertising, Broadstone Pensions and Investments and the Armed Forces have all recently recruited Royal Holloway alumni from the Department of Classics.
Fees, funding & scholarships
Home (UK) students tuition fee per year*: £9,250
EU and international students tuition fee per year**: £25,900
Other essential costs***: There are no single associated costs greater than £50 per item on this course
How do I pay for it? Find out more about funding options, including loans, scholarships and bursaries. UK students who have already taken out a tuition fee loan for undergraduate study should check their eligibility for additional funding directly with the relevant awards body.
*The tuition fee for UK undergraduates is controlled by Government regulations. The fee for the academic year 2024/25 is £9,250 and is provided here as a guide. The fee for UK undergraduates starting in 2025/26 has not yet been set, but will be advertised here once confirmed.
**This figure is the fee for EU and international students starting a degree in the academic year 2025/26.
Royal Holloway reserves the right to increase tuition fees annually for overseas fee-paying students. The increase for continuing students who start their degree in 2025/26 will be 5%. For further information see fees and funding and the terms and conditions.
*** These estimated costs relate to studying this particular degree at Royal Holloway during the 2025/26 academic year and are included as a guide. Costs, such as accommodation, food, books and other learning materials and printing, have not been included.